2024.06
The 2024.06 release of Chemical Computing Group's Molecular Operating Environment (MOE) software includes a variety of new features, enhancements and changes that are summarized in this document.
Core System
AmberEHT is a new forcefield introduced in MOE 2024 that:
- Uses MOE 2024's new bond angle and torsion EHT parameterization.
- Is updated to Amber19, with CMAP torsion cross-term corrections.
- Provides support for non-standard nucleic acids and sugars.
 Updated EHT angle and
torsion parameterization. A novel bond angle and torsion
parameterization methodology based on percentage s hybridization
on directional bonds is now used for all forcefield EHT calculations in
MOE. The new parameters have been found to lead to good agreement with
QM geometry predictions. Note: As a consequence, Amber10:EHT
energy terms may differ from those in MOE 2022.02 and earlier.
Updated EHT angle and
torsion parameterization. A novel bond angle and torsion
parameterization methodology based on percentage s hybridization
on directional bonds is now used for all forcefield EHT calculations in
MOE. The new parameters have been found to lead to good agreement with
QM geometry predictions. Note: As a consequence, Amber10:EHT
energy terms may differ from those in MOE 2022.02 and earlier.
 NEW! AmberEHTo Forcefield.
The new AmberEHTo forcefield is similar to the new AmberEHT
forcefield, the difference being that it uses:
NEW! AmberEHTo Forcefield.
The new AmberEHTo forcefield is similar to the new AmberEHT
forcefield, the difference being that it uses:
- EHT for bond lengths, angles, and out-of-plane parameters.
- OpenFF 2.1 (Sage) SMIRKS torsion parameters.
Note that the AMBER CMAP is now saved to PRMTOP files, to correct backbone torsion psi-phi angles in proteins during Amber MD simulations.
 Potential Setup.
A new Selected Atoms Only option on the Parameters tab of the
Potential Setup panel allows for displaying the parameters of
only the atoms currently selected in the system.
Potential Setup.
A new Selected Atoms Only option on the Parameters tab of the
Potential Setup panel allows for displaying the parameters of
only the atoms currently selected in the system.
 Updated pKa model.
The pKa model in MOE was retrained and improved. Note: this may
result in differences from MOE 2022; for example, in protomer
enumeration.
Updated pKa model.
The pKa model in MOE was retrained and improved. Note: this may
result in differences from MOE 2022; for example, in protomer
enumeration.
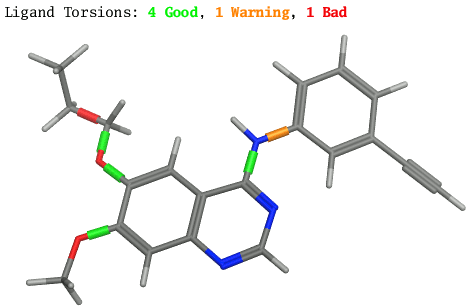
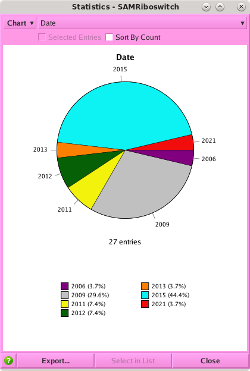
 NEW! Ligand Torsion Analyzer.
MOE | RHS | Ligand | Ligand Torsions
launches a monitor for dynamically assessing the quality of dihedral
angles in the current system based on their consistency with
CSD statistics. Bond sleeves with traffic light coloring are
displayed in the MOE 3D window as quality indicators, along with
a text summary.
Additionally, a Ligand Torsion Analyzer color bar can be displayed
in the MOE footer Dihedral Plot for the currently selected
torsion.
NEW! Ligand Torsion Analyzer.
MOE | RHS | Ligand | Ligand Torsions
launches a monitor for dynamically assessing the quality of dihedral
angles in the current system based on their consistency with
CSD statistics. Bond sleeves with traffic light coloring are
displayed in the MOE 3D window as quality indicators, along with
a text summary.
Additionally, a Ligand Torsion Analyzer color bar can be displayed
in the MOE footer Dihedral Plot for the currently selected
torsion.
 NEW! OpenMOPAC integration.
OpenMOPAC 22.1.1 is now distributed with MOE. MOPAC 7, which was
previously distributed with MOE, is no longer part of the MOE
distribution in 2024.
NEW! OpenMOPAC integration.
OpenMOPAC 22.1.1 is now distributed with MOE. MOPAC 7, which was
previously distributed with MOE, is no longer part of the MOE
distribution in 2024.
OpenMOPAC has been integrated into all applications in MOE that supported the use of MOPAC 7, 2012, or 2016. In particular, support for the MOZYME keyword has been explicitly added to the MOPAC settings page, provided as a Linear Scaling (MOZYME) checkbox.
 NEW! Database Viewer Filters.
NEW! Database Viewer Filters.
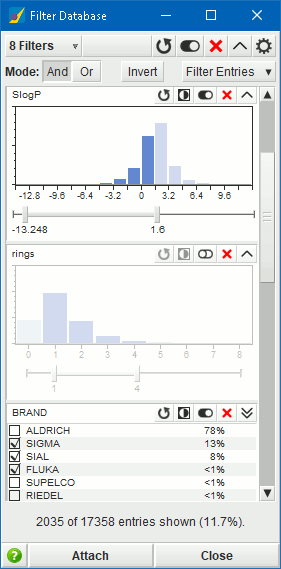 Filter Database, available through either
or the
Filter Database, available through either
or the
 button in the
menu bar of the Database Viewer, provides a quick interactive way to
filter database entries by property. The distributions of database
field values are displayed as histograms or lists of
categorical values, in which a range of values can be specified.
The data display is updated dynamically when any changes
are made to the database contents.
button in the
menu bar of the Database Viewer, provides a quick interactive way to
filter database entries by property. The distributions of database
field values are displayed as histograms or lists of
categorical values, in which a range of values can be specified.
The data display is updated dynamically when any changes
are made to the database contents.
Filter Database provides the following:
- Up to 10 filters.
- Interactive filter adjustment.
- Visual cues to indicate which part of the data are included / excluded by the filtering process.
- Logical AND and OR combining operations.
- Filter inversion (logical NOT operator).
- Set entry selection or visibility based on filters.
- Enable / disable filters.
- Collapsed, summary view of filters.
- Choose whether to use first, minimum, maximum, or average of multi-value database cells.
- Choose whether to always filter out empty cells or cells with non-finite values.
- Attached and detached modes.
 File formats.
Support for the following file formats has been added or enhanced:
File formats.
Support for the following file formats has been added or enhanced:
- The following file formats have been added to the Save panel
():
- mmCIF
- XYZ
- MDB
- Multi-model PDB files can now be written from the Save panel.
- Saving biopolymers (proteins, nucleic acids) as sequences is now available when saving a database as a text or CSV file ().
- Reading of binary CIF files is now supported in the Open panel.
- The AMBER CMAP is now written to PRMTOP files.
 Support for 5-letter
residue names. PDB reading and writing has been updated to support
round-trip preservation of 5-letter residue names in MOE. Long names
are mapped to short names, with the mapping written into
REMARK 99 for recovering the long names on reading.
Reading and writing of REMARK 600 records containing long
residue names is now supported as well.
Support for 5-letter
residue names. PDB reading and writing has been updated to support
round-trip preservation of 5-letter residue names in MOE. Long names
are mapped to short names, with the mapping written into
REMARK 99 for recovering the long names on reading.
Reading and writing of REMARK 600 records containing long
residue names is now supported as well.
 Pi-pi contacts.
The display of π-π interactions (between planar rings) can be
enabled from the popup.
Pi-pi contacts.
The display of π-π interactions (between planar rings) can be
enabled from the popup.
 Ribbon display.
Ribbons have been updated with the following features:
Ribbon display.
Ribbons have been updated with the following features:
- Smooth colors. Ribbon color can be interpolated between differently colored segments.
- Beveled edges. Ribbons displayed using cartoon rendering can be drawn with beveled edges to smooth out the corners.
 System Manager.
The System Manager context menu, opened by right clicking on any of
the lines in the System Manager, now provides a Show 2D
button that shows the corresponding molecule in the 2D
overlay display in the MOE Window.
System Manager.
The System Manager context menu, opened by right clicking on any of
the lines in the System Manager, now provides a Show 2D
button that shows the corresponding molecule in the 2D
overlay display in the MOE Window.
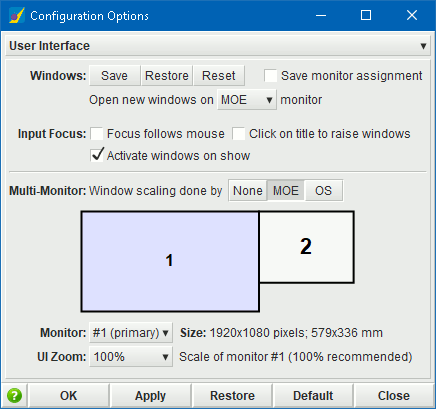
 UI Zoom.
The UI zoom factor of MOE windows can now be done on a per-monitor
as well as a per-window basis:
UI Zoom.
The UI zoom factor of MOE windows can now be done on a per-monitor
as well as a per-window basis:
- Per-monitor zoom. In a multi-monitor system, scaling of individual monitors can be specified in the Configuration Options panel. A schematic in the panel shows the available monitors and their arrangement in the operating system. When scaling to very large sizes, a confirmation dialog will open; if no confirmation is made, the zoom will be reverted after 15 seconds.
- Per-window zoom. Individual MOE windows can be
dynamically zoomed using the following key combinations:
- Zoom out (reduce zoom): Ctrl–, i.e. hold the Control key and press –.
- Zoom in (increase zoom): Ctrl= (or Ctrl+), i.e. hold the Control key and press =.
- Reset zoom: Ctrl0, i.e. hold the Control key and press 0 (zero).
 Bubble Help.
Bubble help in the Database Viewer and Sequence Editor have been
enhanced as follows:
Bubble Help.
Bubble help in the Database Viewer and Sequence Editor have been
enhanced as follows:
- Sequence Editor. The bubble help on non-natural amino acids will now show a 2D depiction of the residue.
- Database Viewer. A new set of Bubble Help buttons in the Database Viewer page of the Configuration Options panel are used to set the display mode of bubble help on minimized molecule cells; the bubble help can be always shown or always hidden, or shown only when a modifier is held down while hovering.
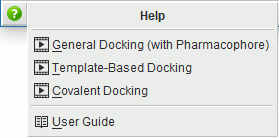
 NEW! Video links.
Context-sensitive video help is now available for many of the panels
in MOE. In addition to the manual page link,
where available, one or more video links will be listed
when the help button is pressed.
If no video links are available, the manual page will open automatically.
NEW! Video links.
Context-sensitive video help is now available for many of the panels
in MOE. In addition to the manual page link,
where available, one or more video links will be listed
when the help button is pressed.
If no video links are available, the manual page will open automatically.
 Selection
expression language. The following updates have been made:
Selection
expression language. The following updates have been made:
- Adding a '?' character suffix when specifying a set name will result in all objects being returned when the set is undefined; without the suffix, no objects are returned.
- The buried and exposed keywords now take a selection expression as an additional optional argument; when specified, the keywords will apply only to the objects defined by the expression.
 Third party
software support. The following software versions are now
supported:
Third party
software support. The following software versions are now
supported:
- Gaussian: g16RevC.01
- AMBER: AMBER 24
- CUDA SDK: CUDA 12
Note that precompiled GPU ptx files are now patchable; i.e. they can be added to the MOE patch and custom directories.
 MOE menus.
The following changes have been made to MOE menus.
MOE menus.
The following changes have been made to MOE menus.
| Menu Name | Menu Item | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MOE | File MOE | RHS |
Capture | Opens the Capture submenu, for accessing the Capture application. |
| MOE | Help | Videos | Opens video.chemcomp.com, which provides on-line access to MOE help videos. |
| MOE | RHS | Ligand | Ligand Torsions | Launches the Ligand Torsion Analyzer, which displays sleeves on torsion bonds colored to indicate quality. |
| DBV | Edit | Filter | Opens Filter Database, for filtering entries in the Database Viewer. |
| DBV | Compute | Protein Patches | Opens the Save Protein Patches panel, for calculating protein patches for structures in the database, and writing them to the database. |
| DBV | Compute | Analysis | Protein Patch 2D Maps | Opens the Protein Patches 2D Maps panel, to display the 2D maps of 3D protein patches that are saved in the database. |
| SE | Alignment | Constraints | Project | <MOE Project name> | Specifies the project from which to obtain alignment constraints. The constraints will be taken from the project reference file. |
Applications
 Conformation Import.
In 2024, Conformation Import was rewritten for better performance and
reliability:
Conformation Import.
In 2024, Conformation Import was rewritten for better performance and
reliability:
- Improved fragmentation rules now create fewer fragments with a better chemical context.
- Penalty functions are used to prevent the generation of unwanted conformations such as, for example, cis-amides.
- Fragment databases are much smaller than in the previous version; fragments were minimized using the new AmberEHT forcefield.
- The panel was streamlined and simplified.
As a consequence of these updates, there almost no failure cases (i.e. where conformations cannot be generated), and calculations are generally much faster than with the previous version.
Note: the output database is now always written with conformations in packed mode.
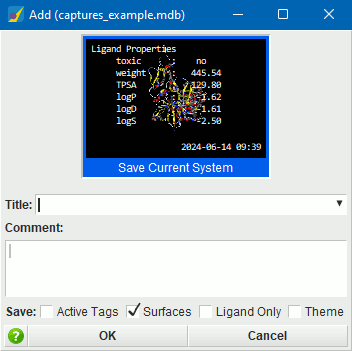
 NEW! Capture.
Capture provides the ability to easily save the current system
along with a title and text annotations – together referred
to as a capture – and subsequently browse and edit
saved captures. Captures are saved to a Capture file which
is specified when the application is launched, and which can be
switched later in the MOE session if desired.
NEW! Capture.
Capture provides the ability to easily save the current system
along with a title and text annotations – together referred
to as a capture – and subsequently browse and edit
saved captures. Captures are saved to a Capture file which
is specified when the application is launched, and which can be
switched later in the MOE session if desired.
Features include:
- provides quick access to Add (add a new capture to the Capture file) and Open (switch Capture files) options, as well as loading from a list of captures. provides the same menu access.
- Attached and detached panel modes. In attached mode, Capture opens in the MOE Footer, with buttons for quick loading, Add, and Edit, and a list popup that includes search, reordering, and delete capability. In detached mode, Capture is launched as a separate panel. The default launch mode is configurable.
- Smooth transitions when loading a capture. The duration of the transition can be configured.
- Save options to specify whether to save only tags with active atoms or only the active ligand, surfaces, and the current theme (view setup). Note that if Ligand Properties are currently displayed, they will be captured too.
- On hover over the Capture footer buttons or Capture list items, bubble help will display a summary of the capture, including a thumbnail of the saved system.
- Traversal between Title and Comment fields using keyboard Tab key. (Use Shift-Tab to enter a text tab.)
 MOEsaic.
MOEsaic, the web-based application for Structure Activity Relationship (SAR)
and Matched Molecular Pair (MMP) analysis, has been enhanced as follows:
MOEsaic.
MOEsaic, the web-based application for Structure Activity Relationship (SAR)
and Matched Molecular Pair (MMP) analysis, has been enhanced as follows:
- Improved Filtering. Filters were fully redesigned. Data distributions are shown as histograms for numerical fields, percentages for categorical fields, and depictions for structure fields. OR and AND combining logic and logical inversion are available.
- Heat Map. The new Heatmap Pane is used to pinpoint where
there may be compounds of interest or not of interest in the
fully enumerated combinations of an R-Group Analysis fragmentation.
Features include:
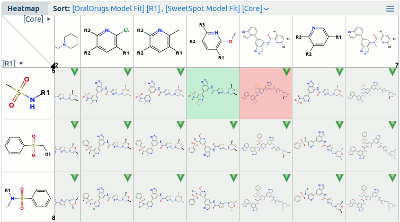
- Dynamic zoom. Using the zoom button in the UI or Ctrl + wheel, the display will zoom in or out. The fully zoomed-in view shows individual fragment and compound depictions. Zooming out loses detail, finally leading to an overview mode in which a sampled view of the data on a regular grid is shown.
- Summary information in bubble help. On mouse hover over the tiles of the heat map display, bubble help will appear with a summary of the data corresponding to that tile.
- Column and row sorting. By default, columns and rows in the display are sorted by the main activity field. Sorting by any field is possible through Sort options in the pane's header.
- Calculate fragment activity using a model. A MOE QSAR model can be used to calculate the activity value of the fragments. If no model is specified, Free Wilson analysis is used to calculate the contribution of each fragment. Fragments can be colored and sorted based on their contribution.
- QSAR models. QSAR models are configured in MOEsaic in
the new Qsar Models page of the Project Configuration panel.
- Upload model files. MOE .fit files can be drag and dropped or selected via a file browser.
- Create model from descriptors. A model can be created or modified manually by selecting descriptors from all available MOE descriptors and then adding them to the model.
- View Templates. The new View Templates pane in the Project Configuration panel allows for specifying custom layouts for each type of tab.
- New plot types. The Plot pane now offers radar plots, box bar plots, and bar charts. These plots are useful for comparing compounds to one another along different property dimensions.
- Custom hooks. Hooks provide a mechanism for quickly and easily sending requests from MOEsaic to third party servers.
- Interaction and pocket surfaces. The Dock pane now generates and displays interaction surfaces and pocket molecular surfaces colored by electrotstatics.
 Protein
structural alignment. The protein structural alignment
methodology in MOE has been redesigned for greater accuracy.
Protein
structural alignment. The protein structural alignment
methodology in MOE has been redesigned for greater accuracy.
- Pairwise protein alignment. The pairwise protein alignment algorithm optimizes the STOVCA alignment quality score, which is based on percentage of aligned alpha carbons.
- Multiple protein alignment. The new multiple alignment method searches for optimal pairwise constraints then builds up a global alignment from the pairwise alignments of each pair of structures using a tree build-up strategy.
- Stuctural Overlap. In , the new Structural Overlap button in the Superpose Options popup specifies that the superposition to be performed will correspond to the calculations used to optimize the protein alignment, i.e. which will maximize the number of equivalenced residues according to STOVCA criteria.
- Pairwise Overlap Scan. This new option in the Align Options popup, when disabled, will perform a faster, less thorough search; this may fail when sequence identity between sequences is low. Enable this option to perform the full search.
 Pharmacophore
Search with subsets.
Pharmacophore Search now support the use of selection expressions
for restricting the pharmacophore search to a subset of atoms of
the system. This makes it possible, for example, to use
pharmacophore search to quickly find protein-protein docking
poses that satisfy particular interaction requirements.
Pharmacophore
Search with subsets.
Pharmacophore Search now support the use of selection expressions
for restricting the pharmacophore search to a subset of atoms of
the system. This makes it possible, for example, to use
pharmacophore search to quickly find protein-protein docking
poses that satisfy particular interaction requirements.
The new Selection option provides the ability to restrict the search by specifying the following sets of atoms:
- Annotate. The atoms that will be annotated for feature matching.
- Bcheck. The atoms to use for a bump check on projected annotations
- Volumes. The atoms to consider during volume checks.
- Molecule. A set of atoms that will be used by default when any of the above sets is left unspecified.
 Pharmacophore Query
Volume Expressions. The Pharmacophore Editor now supports the use of
selection expressions and sets in Volume expressions.
Pharmacophore Query
Volume Expressions. The Pharmacophore Editor now supports the use of
selection expressions and sets in Volume expressions.
 Spectral Analysis.
The Spectral Analysis application has been enhanced with the following
updates:
Spectral Analysis.
The Spectral Analysis application has been enhanced with the following
updates:
- ECD. Electronic Circular Dichroism (ECD) spectra are now available in a new tab. Analogously to the VCD tab where the complementary IR spectra could be displayed, the UV spectrum can be displayed next to the ECD spectrum.
- ORD. Optical rotation dispersion (ORD) is related to ECD via the Kramers-Kronig transformation. ORD spectra can be displayed on the ECD page.
- Conformer Distribution Fitting Weights. When multiple experimental properties are used for fitting, it is now possible to assign a greater or lesser weight to the Chemical Shifts and Coupling Constants contributions. This is useful when it is known that a particular property has greater or lesser accuracy.
- Conformer Distribution 2D display of errors. Similarly to the NMR tab 2D structure display, the Conformer Distribution 2D diagram now shows colored circles scaled by the error of each conformer.
- Duplicate removal RMSD limit. Each tab in the Spectral Analysis panel now provides a configurable RMSD threshold for duplicated removal.
- Averaged calculated shift for CH3. On the NMR tab, calculated H shifts are averaged for methyl groups.
- Save coupling constants. On the NMR tab, the table of coupling constants now offers a Save button.
- Conformer Distribution report. A Create Report button has been added to the Conformer Distribution tab.
- VCD Summary Report. An option has been added to create the VCD report in summary mode.
- Peak Half-Width. On both the VCD and ECD tabs, it is possible now to specify the peak half-width of the selected line shape. This is useful when experimental values might have a lower resolution than the calculated values. By broadening the peak, the theoretical calculation is effectively performed at a coarser resolution, thus potentially providing a better match to the experimental shape.
- Reset Zoom. This button has been added to the NMR, VCD, and ECD tabs.
Note: In Conformation Search, QM duplicate removal is no longer done.
 QuickPrep.
Overwrite Temperature Factor by Displacement is a new
refinement option which, when enabled, overwrites the atom
temperature factor with the distance the atom moved during
minimization, multiplied by 30.0.
QuickPrep.
Overwrite Temperature Factor by Displacement is a new
refinement option which, when enabled, overwrites the atom
temperature factor with the distance the atom moved during
minimization, multiplied by 30.0.
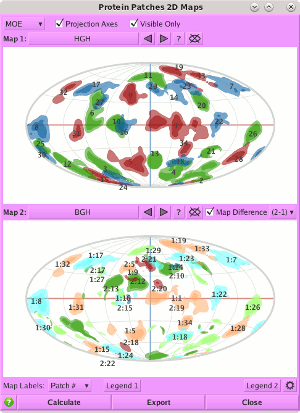
 Protein Patches.
Protein Patches 2D Maps has been enhanced as follows:
Protein Patches.
Protein Patches 2D Maps has been enhanced as follows:
- Map Average. When patches belonging to multiple structures are present in the system, the averaged 2D patches can be displayed by selecting several structures from the list of maps.
- Map Difference. When Map Difference is enabled, the difference between specified maps or averaged maps is displayed.
- Show / Hide. When multiple maps as present, the maps can be displayed in single or double pane mode by showing or hiding one or the other of the map panes.
- Horizontal / Vertical alignment. When both map panes are visible, they can be oriented side-by-side or over-under using the new Horizontal Align setting.
- Legend. Each map pane now has an associated legend popup.
- MDB input. Input structures can now be read from a MOE database file (.mdb).
- Save settings. Panel configurations can be saved and restored.
The Protein Patch Analyzer has a new Area field that reports the cumulative total patch area of all patches listed.
Protein patches can now be calculated over a database. opens the Save Protein Patches panel, in which the type of patch as well as patch parameters can be specified.
 Ensemble Protein
Properties. The following are new features in Protein
Properties:
Ensemble Protein
Properties. The following are new features in Protein
Properties:
- Save patches in database. When enabled, an extra field will be written to the ensemble database containing the protein patches that are generated while calculating patch properties. Note that this may significantly increase the size of the file.
- Save surface. When enabled, an extra field will be written to the ensemble database containing the molecular surfaces of the input structures, colored by a specified ensemble average residue property. The coloring scheme can be configured.
- Subset support. When calculating properties on a database of structures, it is now possible to specify a subset of the system over which to perform calculations, including named sets.
- Environment Charge. The net charge of the fixed (not sampled) part of the system can now be specified. This value is added to the sampled charge for determining the pI of the combined system.
 Epitope Analyzer.
When browsing a database that contains computed epitopes, the
epitope analysis panel is now embedded in the DBV Browser.
Epitope Analyzer.
When browsing a database that contains computed epitopes, the
epitope analysis panel is now embedded in the DBV Browser.
 Protein Design.
Two new options have been added to Protein Design:
Protein Design.
Two new options have been added to Protein Design:
- Preserve Restraints. Tethers, forcefield restraints, and atom fixed state are used to determine whether a residue will be included or excluded from sidechain repacking. This can be used to enforce specific conformations.
- Lower Site Limit. It is now possible to specify the lower limit of Site Limit enumeration.
- Load Mutation Sequence. A sequence file in FastA or raw format can be specified to define the list of mutations.
 Protein Contacts.
Protein Contacts provides new PosA and PosB aggregation
modes. These allow summarizing all interactions for a unique residue
in SetA or SetB, respectively. Since multiple residue contacts and
types may exist, the corresponding interacting pair in PosB or PosA,
respectively, may be a list of residue names/positions.
Protein Contacts.
Protein Contacts provides new PosA and PosB aggregation
modes. These allow summarizing all interactions for a unique residue
in SetA or SetB, respectively. Since multiple residue contacts and
types may exist, the corresponding interacting pair in PosB or PosA,
respectively, may be a list of residue names/positions.
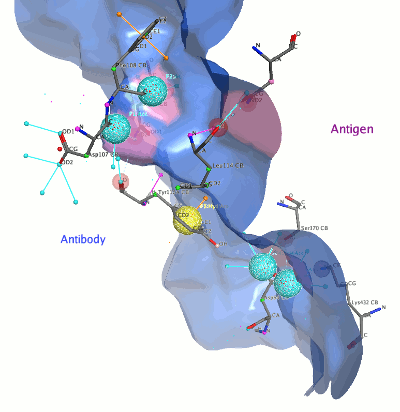
 Pro:Pro Dock.
When the system contains an annotated antibody-antigen complex,
Protein-Protein Docking will now auto-select the antibody as
the ligand, and the antigen as the receptor. $CDR_H3 is
then auto-selected as the ligand site (the active site on the ligand),
and Use Hydrophobic Patch Potential is enabled by default.
"Antibody mode" is enabled through a single
Auto-detect CDR Site Restraints option, which automatically
detects antibody structures and, if found, automatically uses the
CDR H3 loop as an additional site restraint.
Pro:Pro Dock.
When the system contains an annotated antibody-antigen complex,
Protein-Protein Docking will now auto-select the antibody as
the ligand, and the antigen as the receptor. $CDR_H3 is
then auto-selected as the ligand site (the active site on the ligand),
and Use Hydrophobic Patch Potential is enabled by default.
"Antibody mode" is enabled through a single
Auto-detect CDR Site Restraints option, which automatically
detects antibody structures and, if found, automatically uses the
CDR H3 loop as an additional site restraint.
In batch mode, a Verbose Log File can now be specified. Extra progress information is written to this file during the docking run.
 Antibody Modeler.
The Antibody Modeler has the following enhancements:
Antibody Modeler.
The Antibody Modeler has the following enhancements:
- Refinement.
A new refinement protocol is now used to generate the final model.
In a slow-quenching approach, heavy atoms are restrained
and minimized iteratively, which can help improve the stability
of the results.
- Cleave terminal Lysines. When building a full Ig model, the Full Ig Termini option, when enabled, will result in C-terminal Lysine residues being removed prior to adding terminal caps. This option is available only when Model Type is set to Ig.
 MOE project database
RNA support. Support for RNA families has been added to the
following applications in MOE:
MOE project database
RNA support. Support for RNA families has been added to the
following applications in MOE:
- Project Search. Sequence search, substructure search, and general RNA residue handling is now supported in the Project Search panel. Note that remote PSILO families can now be included in Project Search; this is configured from the MOE Configuration Options panel and requires a valid PSILO server to be specified.
- Project building. MOE RNA projects can now be built using Protein Database Update. RFAM codes are supported, with RCSB as the source.
 Database Wash.
The Database Wash application has been enhanced with a
Entropic Filtering option which, when enabled, will result in
protomers with insignificant contributions being removed.
This option is only available when the Protonation mode is set to
Enumerate.
Database Wash.
The Database Wash application has been enhanced with a
Entropic Filtering option which, when enabled, will result in
protomers with insignificant contributions being removed.
This option is only available when the Protonation mode is set to
Enumerate.
Database Wash now also provides a Batch button which can be used to submit Wash jobs to a queueing system, or to perform local calculations at a later time. The application has also been reimplemented to support MPU parallelization.
 Database Correlation.
A new Clipboard button in the Database Correlation panel
copies the correlation matrix R values and field titles onto the text
clipboard in tab-separated form.
Database Correlation.
A new Clipboard button in the Database Correlation panel
copies the correlation matrix R values and field titles onto the text
clipboard in tab-separated form.
 Descriptors.
The following descriptors have been added:
Descriptors.
The following descriptors have been added:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| druglike | Drug-like compound:
150 <= weight <= 600, -1.0 <= logD < 6.0, RBC <= 9 (approximate weight and logD values). Note: in previous versions of MOE, druglike was an alias for lip_druglike. |
| fraglike | Fragment-like compound:
75 <= weight <= 300, -1.0 <= logD < 3.0, RBC <= 3 (approximate weight and logD values). |
| leadlike | Lead-like compound:
150 <= weight <= 450, -1.0 <= logD < 5.0, RBC <= 6 (approximate weight and logD values). Note: in previous versions of MOE, leadlike was an alias for opr_leadlike. |
| organic | Contains only elements found normally in organic molecules, i.e. H, B, C, N, O, F, S, Cl, Br, I, with normal coordination and ionization. |
| PM6_dipole PM6_E PM6_Eele PM6_HF PM6_HOMO PM6_IP PM6_LUMO |
Equivalent to the PM3_* descriptors, but calculated with the PM6 Hamiltonian. |
| PM7_dipole PM7_E PM7_Eele PM7_HF PM7_HOMO PM7_IP PM7_LUMO |
Equivalent to the PM3_* descriptors, but calculated with the PM7 Hamiltonian. |
 Fragment tools.
Several new options have been added to the fragment tools:
Fragment tools.
Several new options have been added to the fragment tools:
- Dominant Protomer. In Scaffold Replacement, Link Multiple Fragments, and Add Group to Ligand, when this option is enabled, the dominant protomer of the generated structure will be output. The result can be output as a 2D depiction, 3D ligand structure, or 3D structure of both the ligand and pocket.
- Create Double Bonds. In Scaffold Replacement, Link Multiple Fragments, and Add Group to Ligand, when this option is enabled, both single and double bonds will be created when making connections, where permitted by geometry and molecular topology.
- Maintain Score. Available in all fragment tools, this option when enabled filters results so that only hits with improved ligand/receptor scores will be retained. Original will output all structures with scores lower than that of the original complex, whereas Maximum will output only structures whose score is better than that of all structures already output up to that point.
- Topologically Unique. This option, already available in several other fragment tools, has now been added to Combinatorial Builder. When enabled, only hits that are topologically unique from all other results up to that point are output.
 AMBER TI.
A dt option has been added to AMBER TI; reduction of dt
can help mitigate AMBER calculation instability. The range
of values is limited to what is reasonable for the simulations.
AMBER TI.
A dt option has been added to AMBER TI; reduction of dt
can help mitigate AMBER calculation instability. The range
of values is limited to what is reasonable for the simulations.
 Solvate.
The following updates have been made to Solvate.
Solvate.
The following updates have been made to Solvate.
- Shape. Two new shapes have been added in Periodic mode: Trunc. Oct. generates images for space group I1 (two images per box) in the shape of a truncated octahedron, and Rh. Dodec. for F1 (four images per box), in the shape of a rhombic dodecahedron.
- Minimize. When enabled, minimization of the atoms in the primitive cell is performed, taking into account lattice symmetry. This can help remove clashes due to non-orthogonal image boundaries with non-primitive unit cells.
- Show Box. For non-primitive periodic cells (e.g. Trunc. Oct. or Rh. Dodec.), display the outline of the of the asymmetric box centered in the periodic cell. Note that this graphic can be toggled on or off using the new Hide Graphics button in the Crystal Parameters panel (the button is available only when a non-primitive periodic cell is in effect).
 Flexible Alignment.
A new Planar Systems are Rigid Bodies option, when enabled,
will enforce that all π systems (connected components consisting
of atoms connected with bonds of high π bond order), will be
treated as rigid bodies.
Flexible Alignment.
A new Planar Systems are Rigid Bodies option, when enabled,
will enforce that all π systems (connected components consisting
of atoms connected with bonds of high π bond order), will be
treated as rigid bodies.
Data Files
 $MOE/lib
files.
The following changes have been made to $MOE/lib:
$MOE/lib
files.
The following changes have been made to $MOE/lib:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| abref/IgC.moe.gz | New Ig constant domain profile for Ig constant domain identification and IMGT constant domain numbering. |
| AmberEHT.ff AmberEHTo.ff ffi_eht.ff ffi_amber.ff |
New forcefield files. |
| cmap.frcmod.gz | AMBER CMAP data file, used when saving the AMBER CMAP to PRMTOP files. |
| frag_chain.mdb frag_ring.mdb |
New fragment libraries for Conformation Import. |
| tor_lib_2020.xml | TorsionLibrary 3.0 created by TorsionPatternMiner. MOE uses the Torsion Library jointly developed by the University of Hamburg, Center for Bioinformatics, Hamburg, Germany and F. Hoffmann-La-Roche Ltd., Basel, Switzerland. |
 Sample molecular data
files. The following changes have been made to
$MOE/sample/mol, the directory of sample molecular data files:
Sample molecular data
files. The following changes have been made to
$MOE/sample/mol, the directory of sample molecular data files:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| 1m17_prepared.moe.gz | New |
| 1yy9_fab.moe | Renamed to 1yy9_fv.moe |
| 3f4h.cif.gz | New |
| 6p4a.cif.gz | New |
|
Dimethyl-L-tartrate_ECD.csv Dimethyl-L-tartrate.moe Dimethyl-L-tartrate_qm.mdb |
New |
| FMN_riboswitch_example.moe.gz | New |
SVL Programming
 The following are SVL functions that have been added to or modified in
MOE. Please consult the SVL Function
Index for more information.
The following are SVL functions that have been added to or modified in
MOE. Please consult the SVL Function
Index for more information.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| db_DisplayAttributes | Get and optionally set Database Viewer display field attributes, such as 'precision', bubblehelp, etc. |
| WindowCreate | On Label and Button widgets, the grScale attribute 'isotropic_shrink' mode has been renamed to 'isotropic-shrink'. Note that in most cases, 'isotropic' is the desired mode. |
| mdl_ParseCTAB | The calling syntax of mdl_ParseCTAB has changed to
allow more detailed accounting of hydrogens. To preserve
original behavior,
mdl_ParseCTAB [lines, qflag]
should be modified to
mdl_ParseCTAB [lines, [query:qflag, hcount:0]]
|
| sm_ExtractUnique | The extracted strings are unique in MOE 2024, but may not
always match those generated in MOE 2022.
To be robust against changes to smiles strings between between
MOE versions,
code that does direct string comparisons of smiles strings
should regenerate them before comparing, using:
smi = sm_ExtractUnique sm_BuildParse smi;
|
| ViewSetup | A new option ribbon_bevel_coeff controls the beveling of cartoon ribbons. The option takes an argument n between 0 and 1 (0 means no beveling). |
 Widgets.
The following attributes have been added to widgets that compose
panels.
Widgets.
The following attributes have been added to widgets that compose
panels.
| Widget | New Attributes |
|---|---|
|
Button Checkbox Radio |
|
| Button |
|
|
FSB FSBText Text |
|
| Listbox |
|
 The following are SVL functions that have been deprecated or removed
from MOE. In brief, all MOPAC 7.0 functions have been removed.
The following are SVL functions that have been deprecated or removed
from MOE. In brief, all MOPAC 7.0 functions have been removed.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| dbv_Minimize | This function no longer exists in MOE. The function db_Minimize can be used instead. |
| el_DefaultGeometry el_EQ el_Energy el_XQ |
These functions no longer exist in MOE. |
| mopac_Run mopac_fread_Output mopac_fwrite_Input mopac_GeometryLines mopac_MolecularOrbital mopac_KeywordLines mopac_Molecule |
These functions no longer exist in MOE. MOPAC can be accessed via the SCF functions. |
Platforms
Windows
The following platforms have been deprecated.
- Windows 7, 8, and 8.1.
Supported Windows platforms are 10 and 11.
Linux
Please note that OpenMOPAC requires glibc 2.14 to run. It is also anticipated that in upcoming releases, the minimum requirement for MOE will also be glibc 2.14, which would imply a minimum requirement of the following platforms:
- RHEL/CentOS 7
- Ubuntu: 12.04 LTS precise
- Debian: 8.0 jessie
- Fedora: 16 verne
- OpenSUS Linux EnterpriseE: 12.1
and the deprecation of the following platforms in upcoming releases:
- RHEL/CentOS 6 and earlier
- Ubuntu: 8.04 LTS hardy and earlier
- Debian: 5.0 lenny and earlier
- Fedora: 8 werewolf and earlier
- OpenSUS Linux EnterpriseE: 11.0 and earlier
These are supported in the current release, but official support may be discontinued in the next release.
Java Version
Note that the minimum Java version required to run MOE is Java 8.
